Atlassian Cloud Backups for Jira and Confluence: A No-Code Approach
Atlassian Cloud Backups are critical for ensuring the safety and availability of your information is crucial, especially when it comes to tools like Jira and Confluence used in project management and team collaboration.
Automating site backups for these platforms is essential for data integrity and business continuity, and thankfully, this can be achieved without needing extensive programming skills.
This blog post aims to summarize the reasons, process, and tools necessary for automating Atlassian Cloud backups, along with their benefits and limitations.
Why Automate Backups for Jira and Confluence
- Data Security: Protects against data loss due to human error, system failures, or cyber attacks.
- Consistency and Reliability: Ensures regular and consistent backups, reducing the risk of outdated or missing data.
- Efficiency: Saves time and resources compared to manual backups, allowing teams to focus on core tasks.
The Process of Atlassian Cloud Backups
- Identify Backup Requirements: Determine the frequency, type of data, and storage location for your backups.
- Choose the Right Tools: Select backup tools that support Atlassian Cloud, such as Rewind, BackHub, or native cloud storage solutions like AWS or Azure.
- Configure Backup Settings: Set up the backup tool according to your requirements, specifying the frequency and scope of the backups.
- Test the Backup Process: Run test backups to ensure everything is working as expected and data can be successfully restored.
Setting up Automation
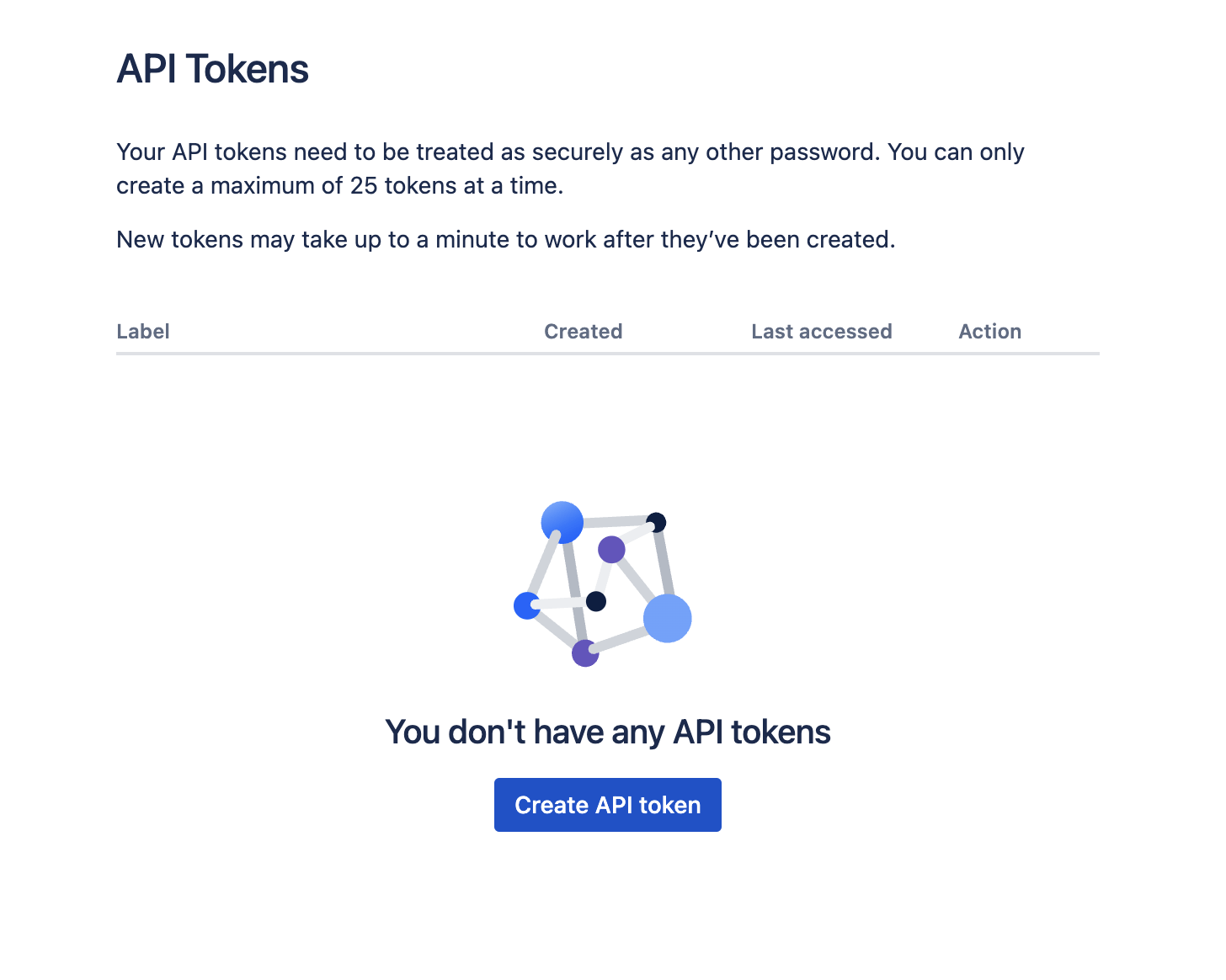
Step 1: Issue an API token of the site-admins account at https://id.atlassian.com/manage/api-tokens
Format should follow ‘$EMAIL_ADDRESS:$API_TOKEN’, into a base64 encoded string.
When creating the string be careful to avoid adding a line break at the end of the encoding.
You can also use a Base64 Encoder.
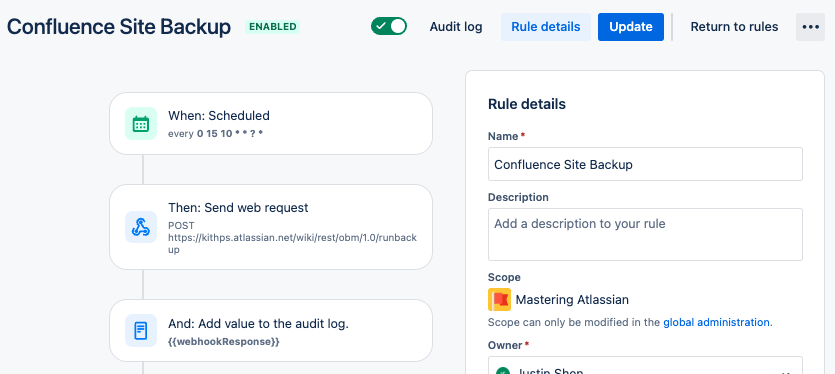
Step 2: General Set up
Start by selecting schedklue for site back up for Jira or Confluence. Example steps below for Confluence
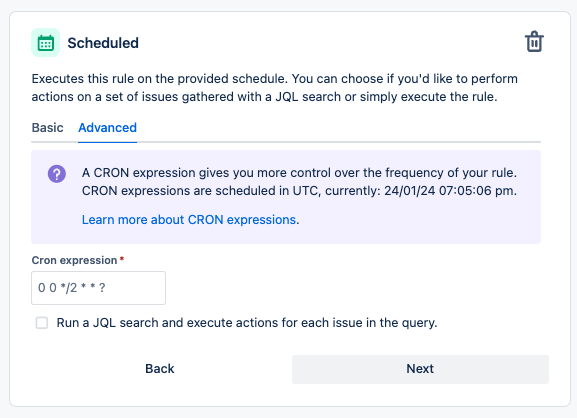
- Set up the schedule and add a Cron expression.
- Select “simply run the conditions and actions without providing issues” for when the rule executes.
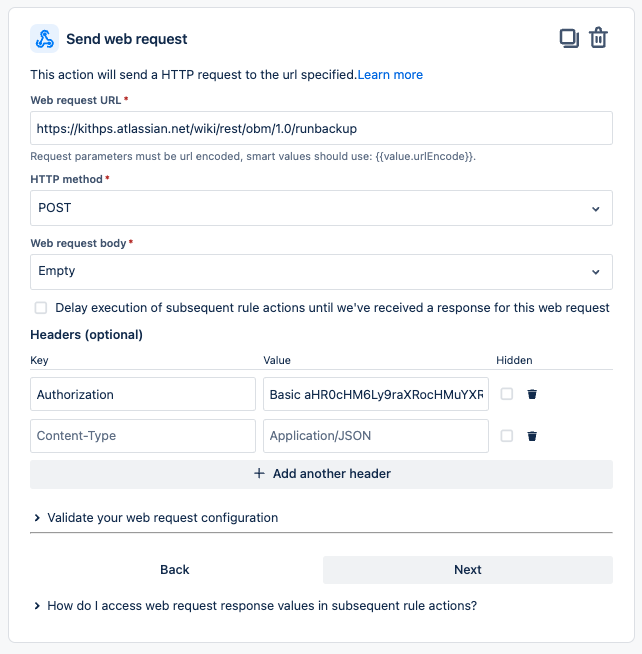
- Add an action – Send web requests:
- Webhook URL: {{baseUrl}}/wiki/rest/obm/1.0/runbackup
- Headers: Authorization: Basic <The output from (1-2)>
- Webhook body: Refer to (2-2).
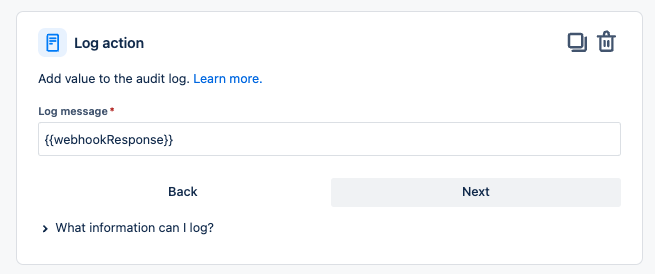
- Add another action – Log action and specify {{webhookResponse}} in the Log message.
- Name the rule “Site backup – Confluence Cloud” and save changes you have made
- Perform a test run using the [Run rule] button.
- When you test the rule, histroy will be saved in the audit log
- Check the download link for the backup in Confluence.
Setting up for Jira is the same with these changes.
- Schedule – same as above
- Action – Send web request
- Webhook URL: {{baseUrl}}/rest/backup/1/export/runbackup
- Webhook body:{“cbAttachments”:”true”, “exportToCloud”:”true”}
- Remaining procedures – same as above
That’s it! You’ve successfully set up custom automations using Jira Automation for Backups.
Conclusion:
Automating backups is a game-changer for teams looking to optimize their time and productivity. By eliminating the need for manual intervention, automated backup solutions ensure data protection is consistently maintained without the risk of human error. This newfound reliability not only safeguards critical information but also frees up team members to focus on strategic tasks, fostering innovation and efficiency. Moreover, in times of unexpected data loss or system failures, automated backups act as a safety net, enabling swift recovery and minimal downtime. Embracing automation is not just a time-saver; it’s a strategic move that empowers teams to excel in a data-driven world.
If you found this useful check out this article from Atlassian too!
Thanks for visiting, click here to learn more about out our Atlassian Cloud Services!
